A patient whose doctor left a piece of gauze in his stomach for 14 years has just undergone successful surgery by doctors at 108 Military Central Hospital.
Recently, 108 Central Military Hospital received a female patient (66 years old) transferred from the previous level with a diagnosis of left kidney tumor.
At 108 Military Central Hospital, the patient was fully examined and re-evaluated, with a preoperative diagnosis of a kidney tumor and recurrent renal pelvis stones after surgery to remove stones 14 years ago.
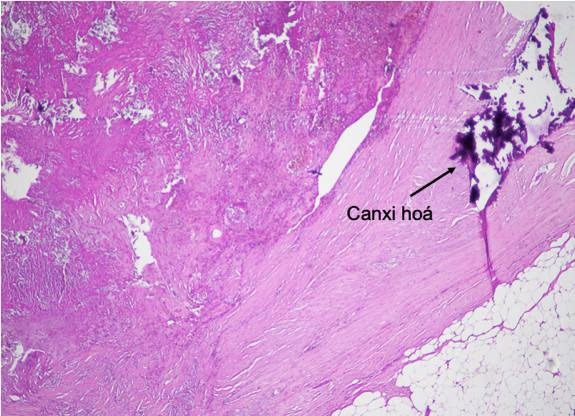 |
| Image of pseudofibroma, calcification |
The patient underwent surgery to remove adhesions, remove the pseudotumor and kidney stones. The post-operative pathology results confirmed that this was a pseudotumor caused by a foreign body - surgical gauze left in the abdominal cavity after a previous surgery.
This is a rare case, the clinical picture is very rare and difficult to evaluate the diagnostic image, leading to an inaccurate diagnosis before surgery. After surgery, the specimen is examined for pathology and combined with the previous surgical history, the pathologists can confirm the correct diagnosis.
According to the patient, the patient had a history of surgery to remove left kidney stones 14 years ago using open surgery. At first, the patient had laparoscopic surgery but encountered difficulties in removing the stones, so the patient was switched to open surgery. During the time after the first kidney stone removal surgery, the patient's health was stable. The patient had no special symptoms.
Recently, the patient went for a health check-up at a higher level and discovered a tumor in the left kidney. On diagnostic imaging, a tumor was found in the upper pole of the kidney, a mixed mass, measuring 30 x 35 mm, pushing the renal capsule, middle renal pelvis, renal pelvis and groups of several stones, the largest measuring 23 mm.
The medulla and cortex were clearly distinguished. The ureter had a diameter of 7mm, the junction of the renal pelvis and left ureter had a stone measuring 9 x 6mm. The patient was transferred to the 108 Military Central Hospital, and the doctors diagnosed before surgery: recurrent renal tumor/renal pelvis stone.
At the 108 Military Central Hospital, the patient underwent surgery to remove adhesions, remove the pseudotumor and kidney stones. The surgery took several hours due to the complexity of the adhesion removal, and the removal of the left kidney and a section of the ureter.
Gross pathological assessment showed that on the periphery of the upper pole of the kidney there was a 3.5cm mass, with a clear boundary with the kidney, pressing on the renal parenchyma, the cross-section of the mass was yellow, the center was crumbly, white, containing foreign bodies such as short white threads and fibers like gauze. Pathological results: Fibrotic inflammation, renal pseudo-tumor degeneration due to foreign bodies.
Dr. Nguyen Viet Hai, Department of Upper Urology, 108 Central Military Hospital said that in this case, the swab was not detected for 14 years, and even after the patient had an imaging test, the diagnosis was not accurate.
In cases where patients have had kidney stones removed, the stones are also likely to recur. Chronic inflammation caused by stones can lead to the formation of cancerous tumors such as urinary tract cancer, squamous cell cancer, etc.
This pseudotumor has evolved over many years, with inflammation, surrounding fibrosis, necrosis, degeneration, and the antler fibers gradually disappearing, making it difficult to detect.
The entire tissue was infiltrated with fibrosis, few inflammatory cells, foreign body giant cells, and some remaining disappeared gauze fibers. The pseudotumor had a clear boundary with the renal parenchyma by a thick fibrous wall and calcified area.
Pathological diagnosis is the final diagnosis that accurately describes the lesion. In addition to the gross characteristics, there are also microscopic characteristics such as the entire fibrotic tissue... calcified areas.
During surgery, bandages are very important to help absorb blood, allowing surgeons to observe the operating field clearly and conveniently. Doctors and nurses must strictly follow surgical procedures.
The amount of gauze used to absorb the blood will be taken out and counted. In large, long surgeries, the amount of gauze used is large. The stress of the doctors and nurses during the surgery can make it difficult to avoid mistakes.
"Removing foreign objects from the body is mandatory to avoid complications. Remove foreign objects by surgery or endoscopy. Obviously, preventing forgetting gauze or instruments is better than treating complications. Strict monitoring of patient safety can certainly prevent similar situations," added Dr. Nguyen Viet Hai.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/benh-nhan-bi-bo-quen-gac-trong-bung-14-nam-sau-phau-thuat-d218648.html



































































































Comment (0)