What is a blood clot (thrombus)?
According to medical experts, blood clots normally stop bleeding when the body is injured or has a cut. Most of the time, the body will break down blood clots after your wound has healed.
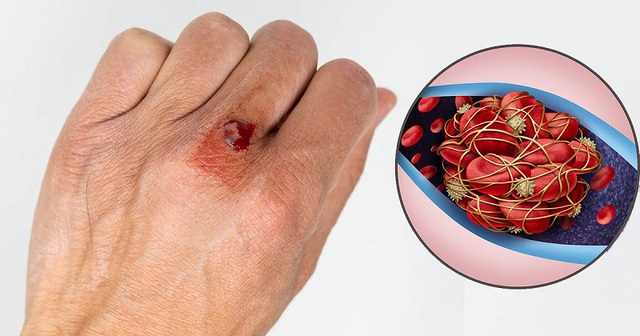
Illustration photo
However, in certain cases, the body cannot clear these blood clots. In the next few times, they will form inside the blood vessels for no apparent reason. Blood clots that block or block blood flow to a part of the brain can cause a stroke.
When a blood clot forms in a blood vessel in the brain, it can block blood flow and cause problems such as a stroke or cerebrovascular accident. This can lead to the loss or damage of areas of the brain and can have serious consequences for brain function.
Signs of blood clot formation in the body
When a blood clot appears in the body, you may not experience any symptoms at first, but when the number of blood clots increases or blocks blood flow, the body will show signs such as: Cold hands or feet; muscle pain or spasms in the affected area; numbness or tingling in the arms and legs; changes in skin color in the area of skin with blood clots.
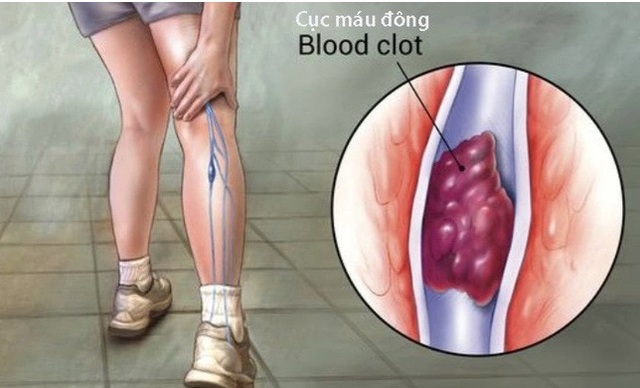
Illustration photo
Causes of blood clots
Blood clots form when blood comes into contact with substances in the blood vessel walls or on the skin. This is a sign that the blood vessel wall has ruptured or the skin surface has been damaged, causing blood cells to leak out.
Additionally, cholesterol plaques (atherosclerotic plaques) form in the arteries, and when these plaques break off, they trigger blood clotting. Most strokes and heart attacks occur when a plaque in the brain or heart suddenly ruptures.
Most blood clots form because of abnormal blood flow in the body. If they are in the heart or blood vessels, platelets can stick together. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and atrial fibrillation are two conditions that cause blood clots because of slow blood flow.
What can be done to prevent blood clots?
You can proactively prevent blood clots from forming by making the following daily lifestyle changes:
Exercise regularly
Exercise and physical activity at appropriate intensity helps improve blood circulation, reducing the risk of obesity and diabetes - factors that can lead to blood clots. Patients should avoid sitting or lying down for long periods of time, and if possible, should exercise gently for about 30 minutes a day.
Limit smoking and alcohol
Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can increase the risk of blood clots and interfere with drug treatment. Therefore, limiting or eliminating these factors will help reduce the risk of blood clots.
Supplement beneficial foods
Foods rich in nutrients that protect blood vessels, such as onions, seaweed, soybeans, ginger, wood ear mushrooms, turmeric, and garlic, can help prevent atherosclerosis, reducing the risk of blood vessel rupture. Controlling the amount of fat in the diet is also important to reduce the risk of blood clots.
6 familiar foods you should eat to prevent blood clots
Illustration photo
Wood ear
Black fungus contains vitamin K, calcium and other nutrients, which can effectively inhibit internal hematoma and prevent blood clots from growing larger. The incidence of thrombosis or blood clots is common in middle-aged and elderly people, so it is recommended that these groups of people eat more black fungus.
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, an active ingredient with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Curcumin may help prevent blood clots by inhibiting platelets from sticking together and reducing plaque buildup in blood vessels.
Curcumin also helps improve blood circulation and may help reduce the levels of inflammatory factors in the body, thereby reducing the risk of developing vascular-related diseases such as stroke.
Race
Ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, which can help prevent blood clots. The active ingredient gingerol in ginger can reduce thromboxane, a hormone that causes platelets to clump together, thereby reducing the likelihood of blood clots forming in the blood vessels.
Ginger can also help remove waste and toxins from our blood, which is beneficial in maintaining the stability of blood vessels. Additionally, ginger also contains salicylates, the same substance that gives aspirin its blood-thinning properties.
Garlic
According to Medical News Today, a 2020 study found that adding garlic to the diet of people with high blood pressure helps reduce blood pressure and has mild anti-thrombotic effects. Therefore, garlic is also not recommended to eat before surgery because it can affect platelet function and blood clotting activity.
Cinnamon
Laboratory and animal studies have shown that cinnamon contains coumarin, which is effective in preventing blood clots. Warfarin, an anticoagulant, is also derived from coumarin. However, more human studies are needed to understand the necessary dosage and contraindications.
Ginkgo biloba
Ginkgo biloba, also known by its scientific name Ginkgo biloba, contains flavonoid and terpenoid compounds with powerful antioxidant properties, which may help improve blood circulation and protect blood vessels as well as memory problems.
Specifically, ginkgo biloba may help prevent platelet aggregation and therefore reduce the likelihood of blood clots forming in blood vessels. This reduces the risk of developing serious conditions such as stroke and heart attack.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/bat-ngo-6-thuc-pham-re-tien-lam-tan-cuc-mau-dong-nguoi-viet-nen-an-de-phong-dot-quy-17224052113162452.htm







![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the 15th meeting of the Central Emulation and Reward Council](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F11%2F27%2F1764245150205_dsc-1922-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
































































































Comment (0)