Here is an analysis of this issue by George Chen - Managing Director and Co-Chair of the Digital Practice at The Asia Group, a policy and business consulting firm, on SCMP.
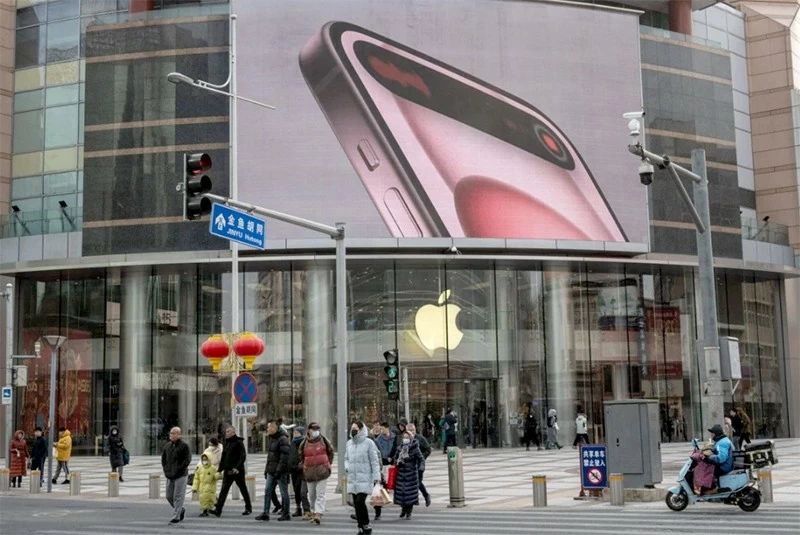 |
| An Apple store in Beijing. Apple phones, once an undisputed status symbol among young Chinese, have seen their market share in China erode significantly. Photo: Bloomberg |
Since its launch more than 17 years ago, Apple’s iPhone has become more than just a smartphone for Chinese consumers – it’s a status symbol. This is especially true for China’s younger generation, who grew up with American cultural influences from drinking Coca-Cola to watching Hollywood movies when Beijing opened its economy to foreign investment in the early 1980s.
However, the iPhone's appeal has recently waned, and Apple, the world's leading consumer technology company, is losing its appeal in China.
Apple has seen its market share erode significantly. For the first time in the second quarter of this year, the top five best-selling smartphones in China were all domestic brands. The top five were Vivo, followed by Oppo, Honor (Huawei’s premium sister brand), Huawei, and Xiaomi. Apple dropped to sixth place, with just 14% market share.
So what has changed? Geopolitics, and in particular US-China tensions, have hurt Apple’s business in China. Beijing has stepped up propaganda in recent years to favor domestic brands. It is now also reportedly asking government officials and state-owned enterprise employees not to use iPhones or other foreign brands, allegedly for national security reasons.
Apple may be partly to blame for this situation. Chinese phone makers such as Huawei Technologies and Xiaomi have invested heavily in their products, including integrating Leica camera lenses and imaging technology to improve image quality — catering to Chinese consumers who value photography.
Industry analysts have expressed concern about the lack of innovation in the iPhone in recent years, especially as the price of a low-cost iPhone now rivals that of some laptops. Chinese-branded phones typically cost one-third to one-half the price of an iPhone, putting Apple in a difficult position amid weakening consumer sentiment.
A similar price war is playing out in the electric vehicle (EV) market, where BYD and other domestic EV makers are slashing prices to compete with foreign brands like Tesla. China is the world’s largest auto market by vehicle sales.
Chinese consumers are becoming more discerning and pragmatic; they no longer consider foreign tech brands like Apple to be “premium.” Meanwhile, Chinese brands have made significant strides in quality and innovation over the past decade.
Even US tech leaders acknowledge this trend of innovation. Meta founder and CEO Mark Zuckerberg has said he should learn from WeChat, often called China's "super app," which excels at messaging, social media, payments and dozens of other online services.
For Apple and other foreign brands hoping to retain the loyalty of Chinese consumers, understanding and embracing localization is crucial. Chinese consumers are now looking for products that fit their everyday needs. For smartphones, they prioritize features like superior image quality and seamless integration with essential Chinese apps for local payments, e-commerce and public transportation.
Apple’s lack of localization may have something to do with the company’s centralized corporate culture. Major decisions from design to marketing are made at the company’s headquarters in Cupertino, California. For Apple, China is the assembly line.
Beijing-based Xiaomi, the world's third-largest smartphone vendor in the second quarter of this year, according to research firm International Data Corporation (IDC), is expected to launch the Mix Flip, its first clamshell phone, and the Mix Fold 4, which features a slim book-like design that can open horizontally into tablet mode, according to teasers released by the company. Photo: Xiaomi
While Apple continues to lose market share in China, Chinese smartphone brands are gaining more consumers globally. Samsung and Apple remain the world's top two smartphone brands by shipments, but Xiaomi has been quickly catching up, narrowing the gap in market share. By the end of the second quarter of this year, Xiaomi had 14.8 percent of the global market compared to Apple's 15.8 percent, according to the International Data Corporation.
Apple is set to launch its iPhone 16 series on September 9, introducing a new generation of iPhones powered by Apple’s artificial intelligence (AI) product, called Apple Intelligence. This is a new opportunity for Apple to win back the favor of Chinese consumers. But it could also pose a new risk for Apple. If the company fails to prove that its AI can work effectively in China — a market known for its strict internet regulations — Apple could face the risk of losing more smartphone market share in China.
Huawei already has its own AI system, while other Chinese brands may partner with major Chinese AI developers like Baidu, Alibaba Group Holding and Tencent to develop AI capabilities on their smartphones.
Apple’s road ahead in China looks challenging, with the company having to increase its focus on localization amid increasingly complex geopolitical tensions.
Source: https://baoquocte.vn/bai-hoc-cho-apple-de-khong-mat-dan-suc-hut-nhu-o-thi-truong-trung-quoc-284309.html


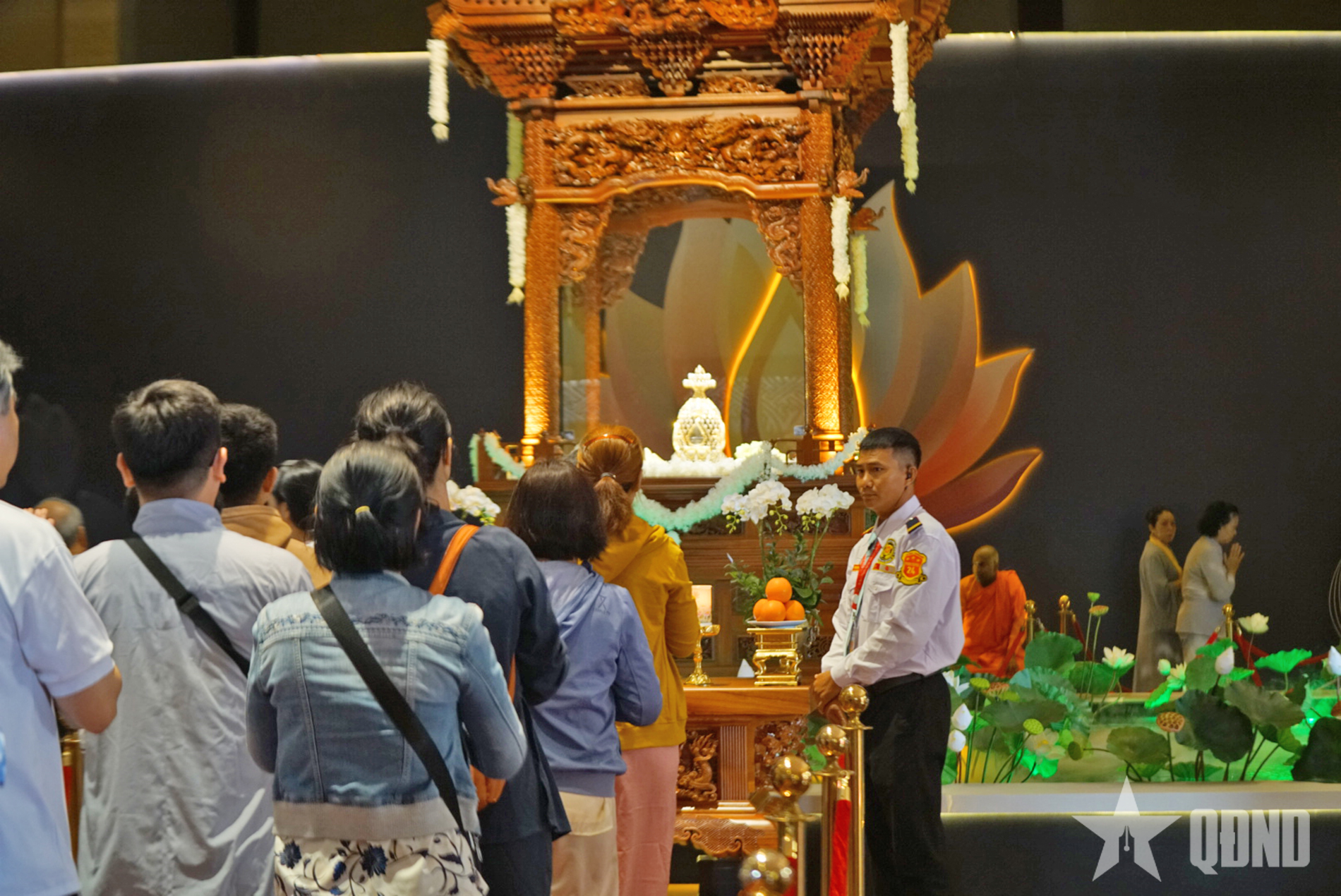
![[Photo] Thousands of Buddhists wait to worship Buddha's relics in Binh Chanh district](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/3/e25a3fc76a6b41a5ac5ddb93627f4a7a)




























































































Comment (0)