Proteins are made up of more than 20 types of amino acids. However, the human body can only produce 9 of them. This group is called essential amino acids. Therefore, to help the body function properly, it needs to obtain the remaining amino acids through food, according to the American website Eating Well .

Long-term protein deficiency will affect the bones' ability to absorb calcium and make them more susceptible to fracture.
Therefore, eating enough protein is essential for health. The US National Institutes of Health recommends consuming about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This amount of protein can come from plants and animals. If you do not consume enough protein, your skeletal muscles will show the following signs of instability:
Muscles shrink
For gym-goers, consuming enough protein helps muscles grow and develop. Similarly, a diet lacking in protein will cause muscles to shrink.
The reason is that when the body lacks protein for activity, it mobilizes the protein already available in the muscles. This mechanism is why a protein-deficient diet in athletes will cause muscle shrinkage.
Weakness and fatigue
A meal or a day lacking protein won't have a major impact on health. However, if this continues for a long time, it can not only cause muscle shrinkage and reduced muscle mass but also lead to fatigue. It can even make everyday activities like climbing stairs or maintaining balance more difficult.
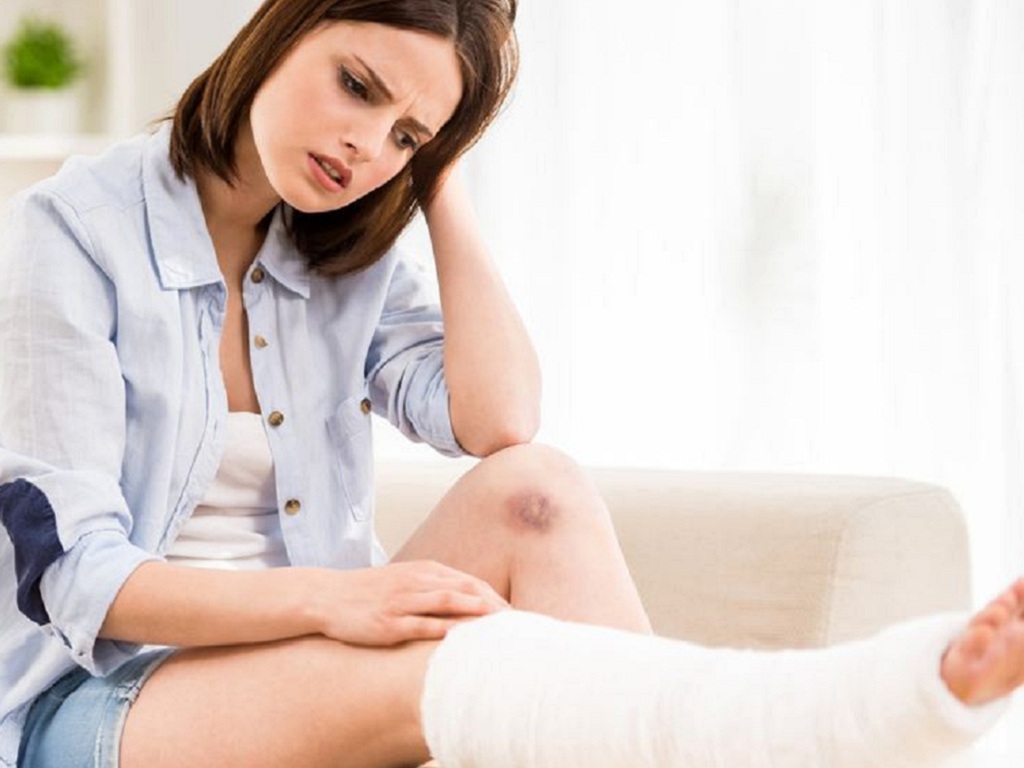
Bones are easily broken.
When we talk about bones, most of us think of calcium. This is not surprising, as strong bones require sufficient calcium. However, in reality, protein plays an equally important role.
Approximately 50% of bone volume is protein. Therefore, protein plays an extremely important role in bone health. Without sufficient protein intake, bones become more prone to fractures.
Furthermore, a study in the Journal of Nutrition showed that adequate protein intake plays a crucial role in the body's ability to absorb calcium. Therefore, a lack of protein will reduce the amount of calcium absorbed into the bones. If this situation persists, it will lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures, according to Eating Well .
Source link

































![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)




































































Comment (0)